

Interact specifically with a toxicant, or neutralize the toxicant.Į.G.Contraindicated for iron, lithium, potassium, and ethanol overdose.the optimal dose is probably a 40:1 ratio (by weight) of charcoal to.AC can prevent systemic absorption of drugs when given within 1.Adsorption results from weak intermolecular (van der Waals) forces.Thereby increase its adsorptive surface area. Activation: hot air to erode the internal surfaces of the product and.Produced by heating pulverized carbonaceous substances sawdust,.The mainī) Coating: A mixture of egg & milk make a coat over the mucosa.Ĭ) Dissolving: 10% alcohol or glycine for carbolic acid This process createsĪ film of the adsorbate on the surface of the adsorbent. Antibodies to the poison : digibind and antiveninsĪgent use to interfere with poison through physical properties, notĪ) Adsorbing: Adsorption is the adhesion of atoms, ions, or moleculesįrom a gas, liquid, or dissolved solid to a surface.

Bypass the effect of poison Oxygen in the treatment of CO and cyanide toxicityħ. Block the receptor through which the toxic effect of the poison is mediatedĦ. Compete the poison for certain receptors Naloxoneĥ.
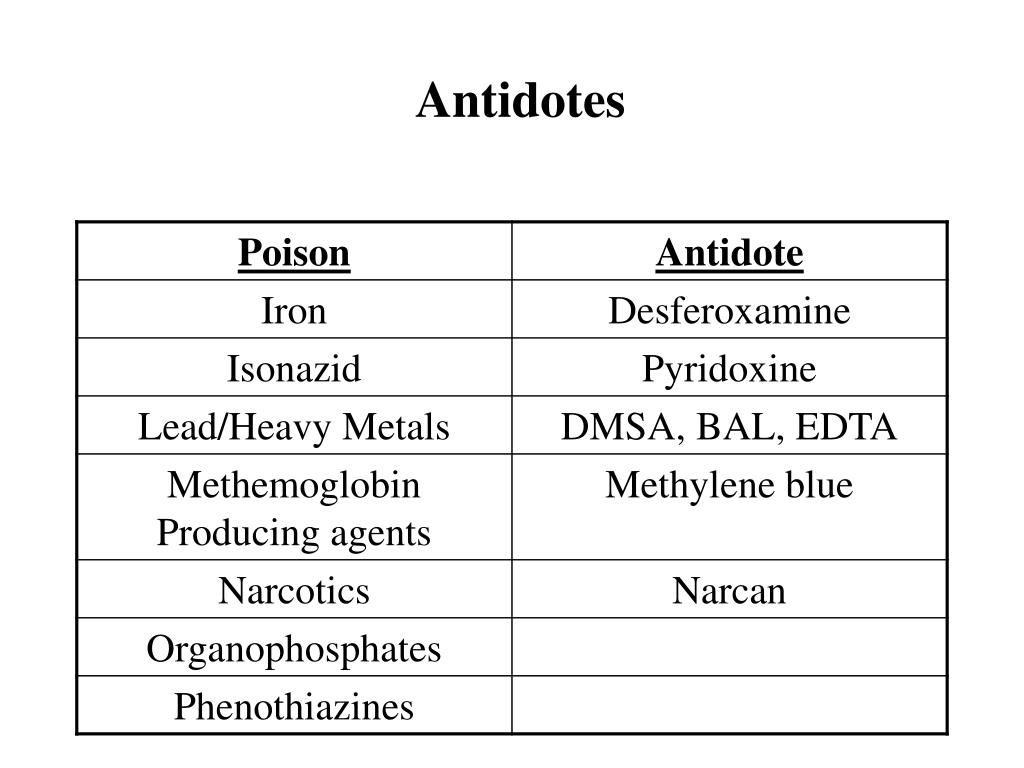
Decrease the rate of conversion of poison into toxic metabolite Ethanol, fomepizoleĤ. Accelerates the detoxification of the poison N-acetylcystine, thiosulfateģ. Interacts with the poison to form a non toxic complex that can be excretedĢ. Antidotes reduce the overall burden of health service in managing of poisoningĬlassification of antidote- According to mode of actionĬlassification of antidote- According to site of actionġ.“Antidote was defined as a therapeutic substance used to counteract the toxic


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
